Trading ladder options is somewhat similar to border options. While in limit options two limits are offered – one upper limit and one lower limit, with ladder options there are generally five price limits (the exact number will depend on the broker and the asset).
These limits are not always distributed symmetrically to the current price level. This means that all five limits can be below the current price level, or that 3 limits can be higher than the current price level and 2 can be lower, for example. The limits were generally traded in both up and down directions – but not always.
All the price limits have two options to trade with – ‘Above’ or ‘Below’ (perhaps represented as ‘Call’ or ‘Put’ by some binary options brokers). Each limit has a different payout percentage for the ‘Above’ and ‘Bottom’ options. The percentage depends on the probability that the prediction is ‘in the money’ (correct). If the probability of the prediction being true is high, the percentage payout is small and vice versa. That’s how learning options can pay out over 1000% and more; the high payout reflects the low probability of them making money.
The limits – or ‘tracks’ – are defined by the brokers and cannot be changed. However, the expiration time can be changed. As the expiration time is modified, there is a corresponding change in the limits and their potential payout.
Ladder Option – Example
Check out the screenshot below. On the right is a range of values – each with its own ‘Above’ and ‘Bottom’ payout figure.
The payout amounts are relative to the $25 entered in the amount field. Each ‘turn’ on the ladder has a different value, and each requires a certain price movement from the actual asset price. The bigger the price movement, the bigger the payout. In the picture, AUD/USD is trading at 0.7403. If you expect a big rise in the price, you can pick ‘top’ at the 0.74112 level and get an excellent return of 374% if you are right.
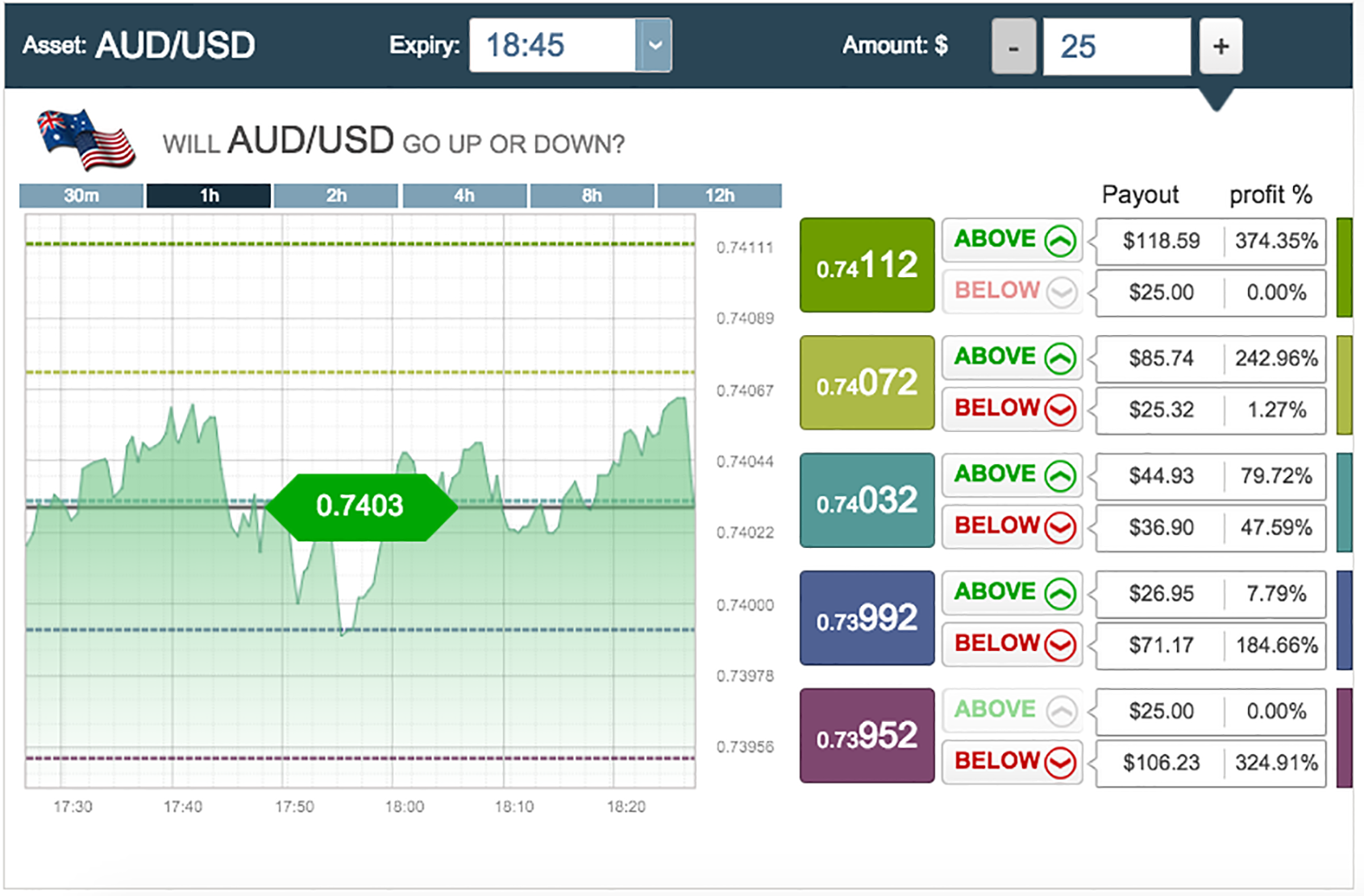
The mid-level option has payouts of 47% for ‘bottom’ and 79% for ‘top’. The options at the very top and bottom have only one option available – above at the highest point and below at the lowest. The broker considers the other outcomes so likely that they are not willing to trade them at all.
Why trade on the ladder?
One of the attractions of binary options is its simplicity. Some traders may argue that learning options create a layer of complexity that detracts from the ‘ease of use’ and should therefore be avoided. The view misses some key points;
- Ladder options offer some big payouts, relative to other trade types
- Ladders provide options during volatile markets
- Where traders expect large price swings, a ladder offers higher profitability than a standard binary option
- Ladders are basically no more complicated than a traditional option
- With ladders, high frequency, low risk / low payouts are possible.
The last point is worth expanding on. In the above screenshot, the price level of 0.73992 can be traded up 7.79% – not a huge payout, but if a trader was confident that the rise from this resistance level was assured, it is a quick, low risk route to profit.
Winning Ladder trades
Options for traders require market awareness and some research. Although the same is true for other trading styles, these factors are extremely important for trading in leather. The biggest payout is possible only if you can get a prediction correct, with a low probability. A steep rise/fall is necessary for an extreme prediction to be correct. This can happen if an important event related to the asset occurs. An interest rate announcement or profit warning from a major firm, for example, can cause a large and sudden price correction. Traders must stay aware of all the events to achieve high paying trades.
Similarly, high frequency trades for lower payouts depend on reduced volatility. The higher strike rate required means that errors must be few.
Ladder binary options offer another route for a trader to make a profit, but it must be fully understood. These can be used as a hedging tool or specialize in their own right. No binary options broker will ever offer ladders – prices and payouts must be constantly updated. So choose any possible broker wisely, and if ladders look like an interesting way to make a profit, make sure to choose the right broker.
Ladder Option Strategy
Ladder options offer the highest payouts of all types of binary options. To trade it effectively, you need a good strategy. This article introduces you to three great strategies for learning options.
The three strategies you will learn in this article are:
- Ladders based on the ATR and moving average crossovers
- Use the ATR and the ADX to make negative predictions
- Trade resistance and support levels with learning options
With these three strategies, you will know three different approaches to learning options. By understanding the spectrum of possibilities, you learn to adjust our strategies according to your preference and create the ideal strategy for you.
Strategy 1: Trading Ladders with ATR and Moving Average
When trading a learning option, you face two challenges:
- Predict the direction of the market, and
- Predict the range of the market.
Tackling both challenges with the same tool is difficult. This is why this strategy uses two tools – one for each forecast.
Predict the direction of the market with moving averages
Moving average crossovers are ideal for predicting the direction of the market. Moving averages calculate the average price of the last periods and repeat this process for all periods in your chart. They then graph the results directly, creating a line.
This line moves slower than the market:
- If the market is in an uptrend, the moving average will be based on periods that are lower than the current market price. The moving average will also be higher than the market.
- If the market is in a downtrend, the moving average will be based on periods that are higher than the current market price. The moving average will also be higher than the market.
If the market changes direction, it switches from one side of the moving average to the other, meaning it must cross the moving average. Hence, the crossing of the moving average is an important event that indicates a change in the direction of the market.This is the perfect opportunity for our strategy.
- If the market crosses the moving average upwards, you invest in a learning option that predicts rising prices.
- If the market crosses the moving average downward, you invest in a learning option that predicts falling prices.
Now that you have the direction, all you have to do is predict the potential range of the market. That’s why you need the ATR.
Predict the range of the market with the ATR
The average true range (ATR) is a volatility indicator. It measures the real average distance the market has moved in the past.
Let’s use the example from our basic text on learning options. Assume you are trading the AUD to JPY currency pair with a current price of 91.226. The expiration of your learning option is 1 hour. The ATR has a value of 0.1 on a 10-minute chart, which tells you that the asset has moved an average of 0.05 during recent periods. This value allows you to predict how far the market can move and what strike price you should use for your learning option.
Let’s assume that the asset has just crossed your moving average upwards and you want to invest in rising prices. Your broker offers you these strike prices for your learning option:
| Name | Price Limit | Top payout | Under payout |
| Price level 1 | 91,200 | 54.23% | 92.62% |
| Price level 2 | 91,245 | 90.89% | 55.44% |
| Price level 3 | 91,291 | 158.29% | 31.47% |
| Price level 4 | 91,337 | 280.34% | 11.32% |
| Price level 5 | 91,382 | 530.43% | 1.00% |
| Price level 6 | 91,425 | 1011.23% | 0.00% |
Which of these strike prices is the best choice for a leather option? Let’s go through them one by one.
- Price level 1 (91.2) is lower than the current market price (91.226). Since you are predicting an upward movement, this would be a very safe prediction. However, this will also limit your payout to 54.23 percent. It is not profitable enough.
- Price level 2 (91.245) is higher than the current market price (91.226), but not by much. In a market that moves quickly at 0.05 per period, it takes the market less than one period to reach this price. Since you expect an upward move, this is still a very safe prediction. This gives you a payout of 90.89 percent, which is better than price tier one, but it’s still not much.
- Price level 3 (91.291) is about 1.5 times the value of the ATR (0.05) away from the current market price (91.226). That sounds interesting. Remember: to win your learning option; the market must trade above the strike price one hour from now. You have six periods until that happens (60 minute expiration, ten minute chart). Not all periods of movement point in the same direction, so it is unlikely that the market will reach a strike price six times as far as the ATR’s value. But a strike price in the range of 1.5 times the value of the ATR with a payout of 158.29 percent looks like a relatively safe bet to make a good profit.
- Price level 4 (91.337) is a little more than twice the value of the ATR from the current market price (91.226). In an upward movement, the market is likely to still reach the strike price. This prediction is a little riskier than price level 3, but you get almost twice the payout – 280.34 percent. Most traders prefer this investment.
- Price level 5 (91.382) is a little more than three times the value of the ATR from the current market price (91.226). This is a risky prediction. The market will have to move in the right direction for four out of five periods. If you do get it right, you get an insane payout of 530.43 percent, which means that the profit of one quarter of your trades is still profitable. Risk takers prefer this strike price .
- Price level 6 (91.425) is more than four times the value of the ATR from the current market price (91.226). This prediction is too risky. Although you would get a huge payout of 1011.23 percent, there is almost no chance of the market reaching this target. It will have to move in the right direction for a whole hour. Stay away from this forecast .
With these assessments, the ATR helped you distinguish the hit prices.
- If you like to play it safe, use price level 3.
- If you like to take risks, use price level 5.
- Traders looking for a nice mix of risk and potential take price level 4.
Trade this strategy for a while and monitor your success. You will find that you prefer a certain relationship between the price price range and ATR. In our example, the ATR has a value of 0.05 and there are six periods until the option expires. If all time periods point in the same direction, the market would move about 0.3. Some traders like a strike price that is about half this distance from the current market price. They will invest in price level 5. Other traders may prefer a strike price that is a third of this distance, leading them to invest in price level 3.
Find your own perfect ratio, and you can quickly and easily use the ATR to select the right price level for your learning option.
Strategy 2: Using the ATR and the ADX
In our previous example, we used the ATR to make positive warrants – we predicted what price levels the current move could reach. With this strategy, we want to do the opposite: we want to predict which price levels are beyond the reach of the current movement.
We can achieve this goal without the moving average. There is no need for a signal; we just want to know if a price level is currently out of reach. Instead, we need a bit more precision, which is why we need the Average Directional Indicator Index (ADX).
Let’s use the same example as earlier: you are looking at a 10 minute chart of the AUD vs JPY currency pair with a current price of 91.226. Your broker offers you these strike prices for a learning option with a 60-minute expiration:
| Name | Price Limit | Top payout | Under payout |
| Price level 1 | 91,200 | 54.23% | 92.62% |
| Price level 2 | 91,245 | 90.89% | 55.44% |
| Price level 3 | 91,291 | 158.29% | 31.47% |
| Price level 4 | 91,337 | 280.34% | 11.32% |
| Price level 5 | 91,382 | 530.43% | 1.00% |
| Price level 6 | 91,425 | 1011.23% | 0.00% |
Since we are now making a negative prediction, we need to focus on the below payoff. The important question is what price level the market can reach and at what price level it makes sense to invest. Let’s take a look at each price level:
- Price level 1 (91.200) is lower than the current market price (91.226). This is a bad investment. When you get payouts like this, your broker expects the market to move up. Otherwise they wouldn’t offer such high payouts for below predictions. Therefore, there is no point in investing in falling prices.
- Price Level 2 (91.245) is higher than the current market price (91.226), but not by much. The prediction that the market will trade below this price level is only meaningful if the ATR is unusually low, for example01. Anything else, and this prediction would be too risky. With a payout of 55.44 percent, you should win more than 65 percent of your trades, so this price level is not worth the risk.
- Price level 3 (91.291) is further from the current market price (91.226) but is still very close. This price level would be a possible investment if the value of the ATR was very low, for example 02. The payout of 31.47 percent is interesting for a negative prediction, but you should know that you are making a safe prediction here.< /li>
- Price level 4 (91.337) allows you to make a safe prediction in most market environments. Even if the ATR reads 0.3, the market is unlikely to trade above this price level when your option expires. Some traders even trade this value with an ATR at 0.4, but the relatively low payout of 11.32 percent requires you to make a safe prediction that you can earn a high percentage of your trades.
- Price levels 5 and 6 (91.382 and 91.425) offer 1 percent and 0 percent payouts, respectively. It does not make sense to trade such payouts.
The point of this is that it is difficult to choose the perfect price level based on the ATR alone. In most market environments, you would be able to safely trade price levels five and six, but their low payouts make these price levels useless. All other price levels require you to mix risk and potential. You need another tool to know how to mix these factors. This instrument is the Average Directional Index of Average Direction (ADX).
The ADX evaluates the directional strength of the market on a scale of 0 to 100. Most traders interpret readings below 20 as a lack of direction and readings above 40 as a strong direction. These values help you determine which strike price to use for your learning option:
- If the ADX reads more than 40, then be cautious. When the market has such strong direction, you need to plan for the worst. Assume that all periods before your option expires point in the same direction, and choose the price level with the highest payout outside this range. In our example, there are six periods until your option expires. For example, price level 3 (91.291) is 0.65 from the current market price (91.226). If the ATR reads less than 0.1, that is the price level you should pick.
- If the ADX reads less than 20, go for it. If the market has no direction, it’s time to get the high payouts. Risk takers can even invest in a price level that is as far as the ATR is from the current market price, traders with an average risk tolerance should use a strike price that is twice as far as the ATR reading. In our example, this means that risk experts can even invest in price level 2 when the ATR reads 0.05, which is a relatively high value. All others must decide between price levels 3 and 4. If the ATR is lower, all traders can choose price level 2.
- If the ADX reads between 20 and 40, you are taking moderate risks. If the market has a medium strong direction, your risk should also be medium. Choose an approach between the two examples above. For example, if the ATR reads 0.02, most traders will invest in price level three, which is a safe prediction, but still get a payout of 31.47 percent.
You can also exclude one or two of these market environments from your strategy. Risk-adverse traders may only invest in this strategy if the ADX reads less than 20.
Strategy 3: Trade Resistance / Support with Learning Options
This strategy is ideal for traders who like visual signals more than mathematical calculations. Resistance and support levels are important price levels that the price of an asset cannot break.
For example, assume an asset traded for around £99. It tested the £100 barrier several times but always managed not to break through. In this case, the £100 barrier becomes a resistance. Similarly, if an asset has traded for around £101 but does not fall below £100, the £100 barrier becomes a support level.
In both cases, something seems to be preventing the asset from breaking through the £100 wall. You’ll never know exactly what stops the market, but that’s beside the point. Apparently traders are no longer willing to buy the asset for £100 (in the case of a resistance) or sell the asset (in the case of a support).
That’s all you need to trade a learning option. If the market approaches a resistance line, you wait until the first strike price with a reasonable payout is within reach. Your definition of a reasonable payout is up to you. Most traders want at least 30 percent and a better payout of 50 percent before investing.
If the market moves closer to the resistance / support, you may be able to invest in the same resistance / support with a higher payout. Most traders use this opportunity to earn more money with the same prediction.
If the market breaks through a resistance or support, you will lose all your options. You can solve the lost money. If the market breaks a resistance/support, it has freed itself and is likely to move strongly. This is the ideal environment to invest in a learning option that predicts a strong move. You should easily be able to win a learning option with a payout of 200 percent, which can cover your losses.
Ladders – summary
Ladder options allow for a variety of potential strategies. Depending on your risk tolerance and whether you prefer positive or negative forecasts, you should adjust your strategy according to the three strategies we have outlined. The possibilities are endless, but now you know where to start.
Ladders Binary Options Brokers